Why is Maven more preferable than Simple Java project?
What is this post all about??
Many people are aware of Maven. But if I ask why would you prefer Maven based Java project over simple Java project,
many of you may give just a normal answer like:
“Maven has the ability to download dependencies automatically, based on the dependencies block you put in respective maven project’s pom.xml file”.
Yes, that’s true and its one of the major bonus point of maven based java project. But there are certain other benefits in maven which when utilized fully can help you a lot in managing and implementing your project.
Let me describe you all the benefits of using maven on by one.
So, let’s get started.

Today Maven is a very well known term and most of us use it in our automation projects. Though many of us use this power packed tool called Maven, but very few are aware of its uses and benefits. It has variety of commands available which can easily help you out with your daily tedious tasks.
What is Maven?
Maven is a powerful project management tool that is based on POM(project object model). It is used for projects build, dependency and documentation.
How does Maven solve the following problems we face in project management?
Here is the list of tasks which Maven takes care of and you just need to sit back and enjoy your cup of coffee while Maven is working:
- It adds all the necessary jars to the project as per the dependencies put by user in pom.xml file.
- Automatically creates the right project structure.
- It makes a project easy to build.
- It provides project information like log document, cross references sources, mailing list, dependency list, unit test reports, etc.
- Works with CLI(Command Line Interface).
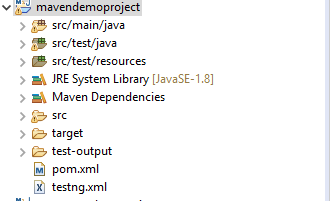
Following is the project structure of maven project:
This structure is automatically created on creating a new maven project.
What is pom.xml?
POM is an acronym for Project Object Model. It contains information about project and configuration of the project such as dependencies, build directory, source directory, test source directory, plugins, goal, etc.
Maven reads pom.xml and then executes goal.
Following is the sample of pom.xml file:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.mfaisalkhatri</groupId>
<artifactId>mavendemoproject</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>mavendemoproject</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.seleniumhq.selenium/selenium-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId>
<artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId>
<version>3.141.59</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.testng/testng -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>6.14.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.github.bonigarcia</groupId>
<artifactId>webdrivermanager</artifactId>
<version>3.7.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.mfaisalkhatri</groupId>
<artifactId>configreader</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.0</version>
<configuration>
<compilerVersion>1.8</compilerVersion>
<source>${maven.compiler.source}</source>
<target>${maven.compiler.target}</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M3</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>test</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<properties>
<property>
<name>usedefaultlisteners</name>
<value> false</value>
</property>
</properties>
<suiteXmlFiles>
<suiteXmlFile>testng.xml</suiteXmlFile>
</suiteXmlFiles>
<argLine>-Dfile.encoding=UTF8 -Xdebug -Xnoagent</argLine>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Once you put dependencies inside the pom.xml file and save it, maven searches for dependency in maven central repository and downloads the jar files accordingly for your project.
Maven Commands:
1. mvn validate : Validate the project is correct and all necessary information is available.
2. mvn compile : Compile the source code of the project.
3. mvn test : Test the compiled source code using a suitable unit testing framework. These tests should not require the code be packaged or deployed.
4. mvn package : Take the compiled code and package it in its distributable format, such as a JAR.
5. mvn integration-test : Process and deploy the package if necessary into an environment where integration tests can be run.
6. mvn verify : Run any checks to verify the package is valid and meets quality criteria.
7. mvn install : Install the package into the local repository, for use as a dependency in other projects locally.
8. mvn deploy : Done in an integration or release environment, copies the final package to the remote repository for sharing with other developers and projects.
There are two other Maven life cycles to note beyond the default list above. They are as follows:
1. mvn clean : Cleans up artifacts created by prior builds.
2. mvn site : Generates site documentation for the project.
Phases are actually mapped to underlying goals. The specific goals executed per phase is dependent upon the packaging type of the project.
You can also run the above commands using life cycles commands for e.g.
1. mvn clean install.
2. mvn clean test
3. mvn clean verify, etc..
The other disadvantage in simple java project is that you cannot run it from CLI. Also, all the packaging and deploying tasks needs to be taken care manually which is a very tedious task.
Hope, you have got the basic knowledge of how maven works and why it would be more preferable than the simple java project. In case if you have any queries, feel free to connect with me here on this site via chat window or DM me on Facebook/Twitter/LinkedIn.